Featured Snippet
Lion’s Mane contains hericenones and erinacines that influence NGF and other pathways linked to nerve health and neurogenesis. Human trials show promising cognitive and mood benefits; animal models demonstrate clear nerve-regeneration effects. Choose high-quality, lab-tested extracts and consult a healthcare professional or our team when in doubt. Start gradually and track how you feel.
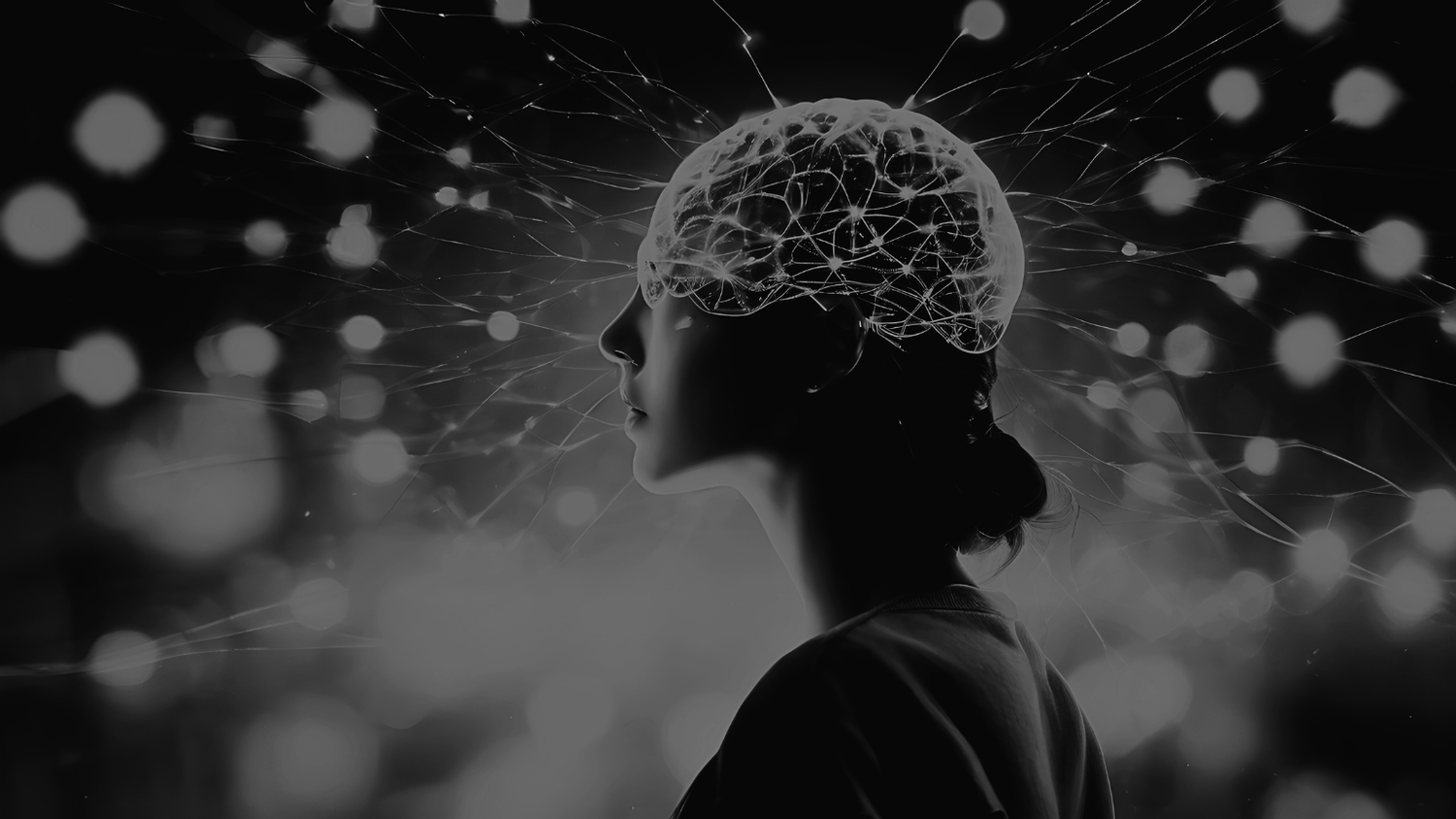
Lion’s Mane sits at the sweet spot between ancient herbal wisdom and modern neuroscience. Monks, chefs and herbalists prized its texture and effects for centuries; today researchers study how its unique compounds might support brain health, neuroplasticity, and even nerve regeneration.
Imagine a mushroom so intriguing that it may encourage the proteins your nerves use to repair themselves. This is not a cure, but a partner in resilience.
This article merges friendly explanation, clinical findings (summarised from clinical studies), and practical guidance for people curious about adding Lion’s Mane to their routine.
Table of Contents

What is Lion’s Mane Mushroom?
Hericium erinaceus is an edible mushroom notable for its white, shaggy “mane” appearance. Traditionally consumed as food and tonic in East Asia, it contains two groups of bioactives often discussed in research: hericenones (found in the fruiting body) and erinacines (found primarily in the mycelium).
💡Did You Know?
These are the compounds interact with neurotrophic pathways and antioxidant systems.
Lion’s Mane: Ancient Wisdom, Modern Curiosity
Lion’s Mane has long been used in Traditional Chinese Medicine as a tonic for the stomach, spleen, and spirit. Monks were known to consume it to sharpen focus during meditation, and in East Asian cuisine, it’s valued not just for its medicinal properties but for its lobster-like texture and umami flavour.
But it’s the mushroom’s potential effect on the brain and nerves that has captured global attention.
While modern nootropics aim to stimulate cognition temporarily, Lion’s Mane does something more foundational. It appears to support the regeneration and repair of neurons, the core wiring of your nervous system.
That’s a bold claim. But research is beginning to uncover the mechanisms that might make it possible.
Understanding Nerve Damage and Repair
Nerve repair is one of the body’s biggest challenges, and this is exactly where interest in Lion’s Mane begins.
Your nervous system is divided into two major branches:
- The central nervous system (CNS): brain and spinal cord
- The peripheral nervous system (PNS): nerves throughout your limbs, organs, and muscles
The CNS has very limited ability to regenerate, meaning damage from injury, inflammation, aging, or disease can persist for years. The PNS can heal, but slowly and often incompletely. Injuries from accidents, surgery, repetitive strain, or metabolic conditions like diabetes may lead to long-lasting numbness, tingling, weakness, or pain.
Nerve damage is often invisible, yet it can influence everything from balance and digestion to sleep, mood, and energy. Over time, unresolved dysfunction contributes to chronic fatigue, cognitive decline, and persistent pain.
Supporting this system isn’t just about restoring sensation, it’s about improving overall quality of life.
This is where Lion’s Mane enters the picture. Early research suggests it may support the body’s own repair mechanisms by encouraging the release of Nerve Growth Factor (NGF), signals that help nerves say, “It’s time to rebuild.”
That’s why Lion’s Mane draws interest not only for recovery, but for anyone wanting to protect and nourish their nervous system as they age.
How Lion’s Mane May Support Nerve Health
Neurotrophic support • Inflammation control

- NGF stimulation: Hericenones and erinacines are linked to increased Nerve Growth Factor (NGF), essential for neuron growth, repair, and maintenance.
- Neurogenesis & plasticity: Preclinical models show increased hippocampal neurogenesis and improved synaptic connectivity, supporting memory and learning.
- Anti-inflammatory & antioxidant action: Polyphenols and triterpenes reduce oxidative stress and inflammatory signalling that can damage nerve tissue.
- Myelin & structural support: Rodent studies suggest potential support for myelin repair, improving nerve signal conduction.
- Gut–brain interaction: Erinacine-enriched extracts may influence cognition indirectly through microbiome modulation.
Lion’s Mane in Human Clinical Studies
Cognition • Mood • Aging support

- Mild Cognitive Impairment (Mori et al., 2009): A 16-week randomized placebo-controlled trial (~3 g/day fruiting body) showed improved cognitive test scores during supplementation, which declined after discontinuation.
- Mood & anxiety (Nagano et al., 2010): A 4-week study reported reductions in mild anxiety and somatic symptoms.
- Aging & cognition (Saitsu et al., 2019): Older adults demonstrated improvements in select memory assessments after 12 weeks.
- Recent pilot trials (2023–2024): Erinacine-enriched mycelium extracts showed faster processing speed and microbiome shifts associated with cognitive outcomes.
Lion's Mane Preclinical Evidence: Nerve Repair & Functional Recovery
The strongest experimental evidence for structural nerve repair comes from animal models.
Highlights:
- Peripheral nerve crush models: Rats treated with Lion’s Mane extract recovered function faster, showed improved gait and axonal regrowth, and upregulated regenerative signalling (Akt/MAPK pathways).
- Sensory restoration & barrier repair: Studies demonstrated faster return of sensory reflexes and repair of the blood–nerve barrier after treatment.
- Diabetic neuropathy & pain models: Erinacine-rich extracts reduced oxidative stress and improved pain thresholds in diabetic and spinal-injury models.
These models show plausible mechanisms for nerve regeneration and functional improvement; important context for translating to human research.
Lion's Mane Fruiting Body vs Mycelium: Which Should You Choose?
Both have value, depending on your goal:
- Fruiting body: richer in hericenones, commonly used in cognition and mood studies.
- Mycelium: contains erinacines such as Erinacine A, shown in preclinical work to cross the blood–brain barrier and exert potent neurotrophic effects.
Some supplements use a combined approach; others target one fraction. Antioxi publishes extraction details and lab testing so you know what actives are present in each batch.
Dosage Recommendation
Typical Lion's Mane extract dosing ranges between 1g and 3g daily, depending on severity and individual response. For Cognitive and Nerve Support, many start at 1g daily and adjust gradually.
Always follow product guidelines and consult with a healthcare professional.

General Safety
Lion’s Mane is generally well tolerated and considered low risk for most people. Reported side effects are mild and uncommon, usually involving digestive discomfort during the first few days of use.
Who Should Use Caution?
- People with allergies to mushrooms: Avoid Lion’s Mane completely if you have known fungal or mushroom allergies.
- Those with autoimmune conditions: Because Lion’s Mane may influence immune activity, individuals with autoimmune disorders should speak to their clinician before supplementation.
-
Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals: Human safety data is not available, so medical guidance is recommended.
Potential Interactions with Lion's Mane
| Medication / Category | Potential Interaction |
|---|---|
| Blood thinners (e.g., warfarin) |
Lion’s Mane may have mild anticoagulant-like effects in some individuals. Those taking blood-thinning medications should consult a healthcare professional before use. |
| Diabetes or blood sugar medication | Some preclinical findings show Lion’s Mane may influence glucose metabolism. If you take glucose-lowering medication, consult your clinician to avoid potential additive effects. |
| SSRIs, SNRIs, or antidepressants | While no harmful interaction is proven, Lion’s Mane may influence mood pathways and neurotrophic factors (such as NGF). Speak to a healthcare provider before combining it with mood-related medications. |
| Immunomodulating drugs | Individuals on prescription immunotherapy, corticosteroids, or immunosuppressants should check with a doctor, as Lion’s Mane may influence immune signalling. |
| Anti-inflammatories (NSAIDs) | Lion’s Mane has its own anti-inflammatory effects. Those taking long-term NSAIDs should consult their clinician if combining both. |
Reminder: “Natural” does not always mean “interaction-free.” If you’re on medication or have a chronic condition, treat Lion’s Mane like any potent botanical, with informed guidance.
Choosing the Right Mushroom Supplement
Quality matters with mushrooms.
✅ Look for extracts made from the fruiting body (not just mycelium)
✅ Verified beta-glucan content and third-party lab testing
✅ Avoid products with fillers or artificial additives
At Antioxi, we prioritize organic, lab-tested extracts to deliver consistent results.
👉Book a Free Consultation with Us.👈 Our team can help you determine the best approach for your needs.
👉 Read our guide to supplement labels before buying.
A Brief Note on Reishi: The Restful Ally
While Lion’s Mane supports cognitive clarity and nerve regeneration, Reishi complements the picture beautifully.

Known for its calming, adaptogenic properties, Reishi helps regulate the nervous system, making it an ideal partner for those dealing with stress-related inflammation, poor sleep, or nervous tension.
If Lion’s Mane is the architect of growth and repair, Reishi is the caretaker, ensuring the system stays grounded and well-regulated.
Final Thoughts: A Mushroom with Meaning
Lion’s Mane isn’t a miracle, but it may be the most meaningful mushroom in the nootropic and neuroregenerative space. Its promise lies not just in isolated studies, but in its harmony with how the body naturally wants to heal.
Take it daily. Track your changes. Let your biology speak for itself.
Frequently Asked Questions for Lion’s Mane & Nerve Health
1. What are the benefits of Lion’s Mane?
Research and traditional use indicate Lion’s Mane may support cognitive function, mood balance, and nerve resilience through NGF-related pathways and antioxidant effects.
2. Can Lion’s Mane help nerve regeneration?
Studies show improved nerve regrowth and functional recovery in peripheral nerve-injury models.
3. What is the recommended dosage?
Common supplemental guidance is 1–3 g/day of extract depending on product concentration. Follow product directions, reach out to our team via chat, email, or book a Free 1:1 Consultation
4. How long before I notice effects?
Some people notice subtle changes within 1–3 weeks; cognitive measures in trials often improved after 8–16 weeks of consistent use.
5. Is Lion’s Mane safe with medications?
It may interact with certain medications (e.g., anticoagulants or immunomodulating drugs). Always consult your healthcare provider before combining supplements with prescription medications.
6. Can Lion’s Mane help neuropathic pain or diabetic neuropathy?
Preclinical models show reduced oxidative stress and improved pain thresholds in neuropathy models, clinical evidence is still in the early stages .
7. What’s the difference between fruiting body and mycelium?
Fruiting body typically contains hericenones; mycelium contains erinacines. Your choice should match your goal, cognitive trials often use fruiting-body extracts, while mycelium extracts can deliver erinacines.
8. Can Lion’s Mane improve mood or reduce anxiety?
Some small human trials report reductions in anxiety and improvements in mood.
9. How does Antioxi extract its Lion’s Mane?
Antioxi uses targeted extraction (fruiting body and/or mycelium depending on the batch), dual-extraction where relevant, and publishes batch COAs for transparency.
References
- Mori K, et al. Randomized double-blind trial: Lion’s Mane and cognitive scores (2009). Summary & outcomes
- Nagano M, et al. 4-week Hericium erinaceus intake: Effects on depression & anxiety (2010). Summary & outcomes
- Saitsu H, et al. Oral intake in healthy adults improves cognition (2019). Summary & outcomes
- Docherty D, et al. Acute & chronic effects on cognition, stress, and mood (2023). Summary & outcomes
- Černelič Bizjak M, et al. Erinacine A, gut–brain axis, cognitive support (2024). Summary & outcomes
- Wong K, et al. Crush injury model: Nerve regeneration in rats (2011). Summary & outcomes
- Yi Y, et al. Diabetic neuropathic pain: Protective effects in rats (2015). Summary & outcomes
- Yang X, et al. Mycelium (Erinacine S) & neuropathic pain mechanisms (2020). Summary & outcomes
- Wong K, et al. Sensory function restoration & blood-nerve barrier repair (2012). Summary & outcomes
Continue Exploring
Dive deeper into mushroom supplements for menopause wisdom with our expert blogs and FAQs, and shop Antioxi’s premium blends and extracts crafted for maximum safety & potency.























1 comment
Joseph O'Brien
My partner got nerve damage from a reaction to the MRNA covid vaccine. Has lost some feeling in fingertips that make it hard to grasp things. This was back in 2021. Is it too late to start on Lion’s Mane?
Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.